java.lang.classloader
A class loader is an object that is responsible for loading classes. The class ClassLoader is an abstract class. Given the name of a class, a class loader should attempt to locate or generate data that constitutes a definition for the class. A typical strategy is to transform the name into a file name and then read a “class file” of that name from a file system.
Every Class object contains a getClassLoader() reference to the ClassLoader that defined it.
Applications implement subclasses of ClassLoader in order to extend the manner in which the Java virtual machine dynamically loads classes.
The ClassLoader class uses a delegation model to search for classes and resources. Each instance of ClassLoader has an associated parent class loader. When requested to find a class or resource, a ClassLoader instance will delegate the search for the class or resource to its parent class loader before attempting to find the class or resource itself. The virtual machine’s built-in class loader, called the “bootstrap class loader”, does not itself have a parent but may serve as the parent of a ClassLoader instance.
上面是Android API 26 Platform中ClassLoader类中的部分注释说明。Java和android中的类加载机制中ClassLoader类都是作为基础类存在。
java中系统classloader类的继承关系如下:
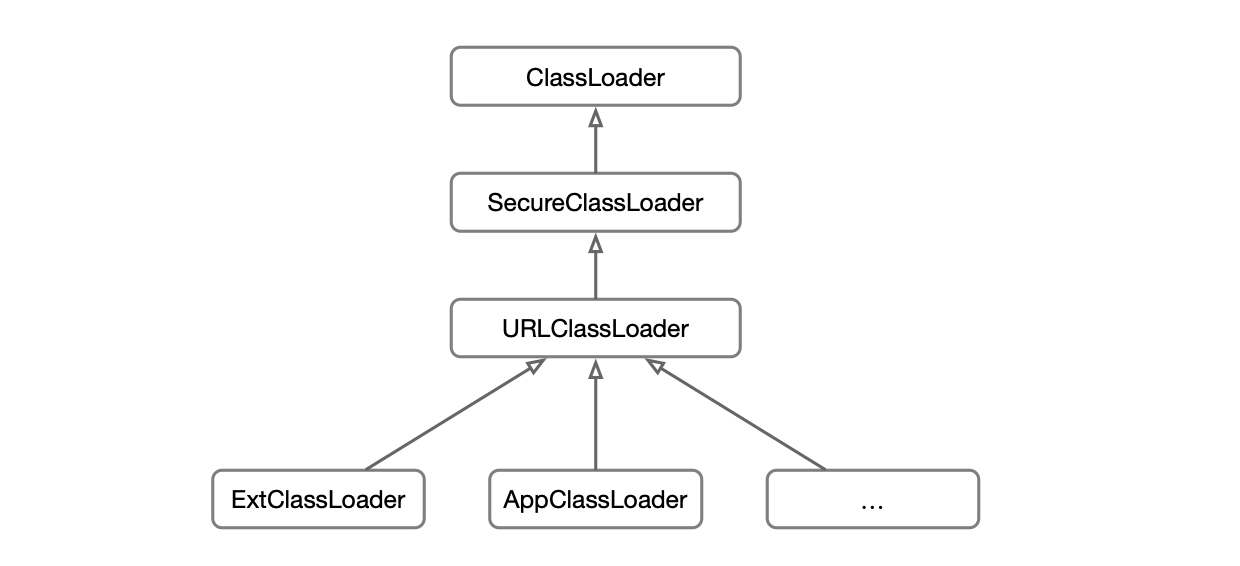
Android中系统classloader类的继承关系如下:
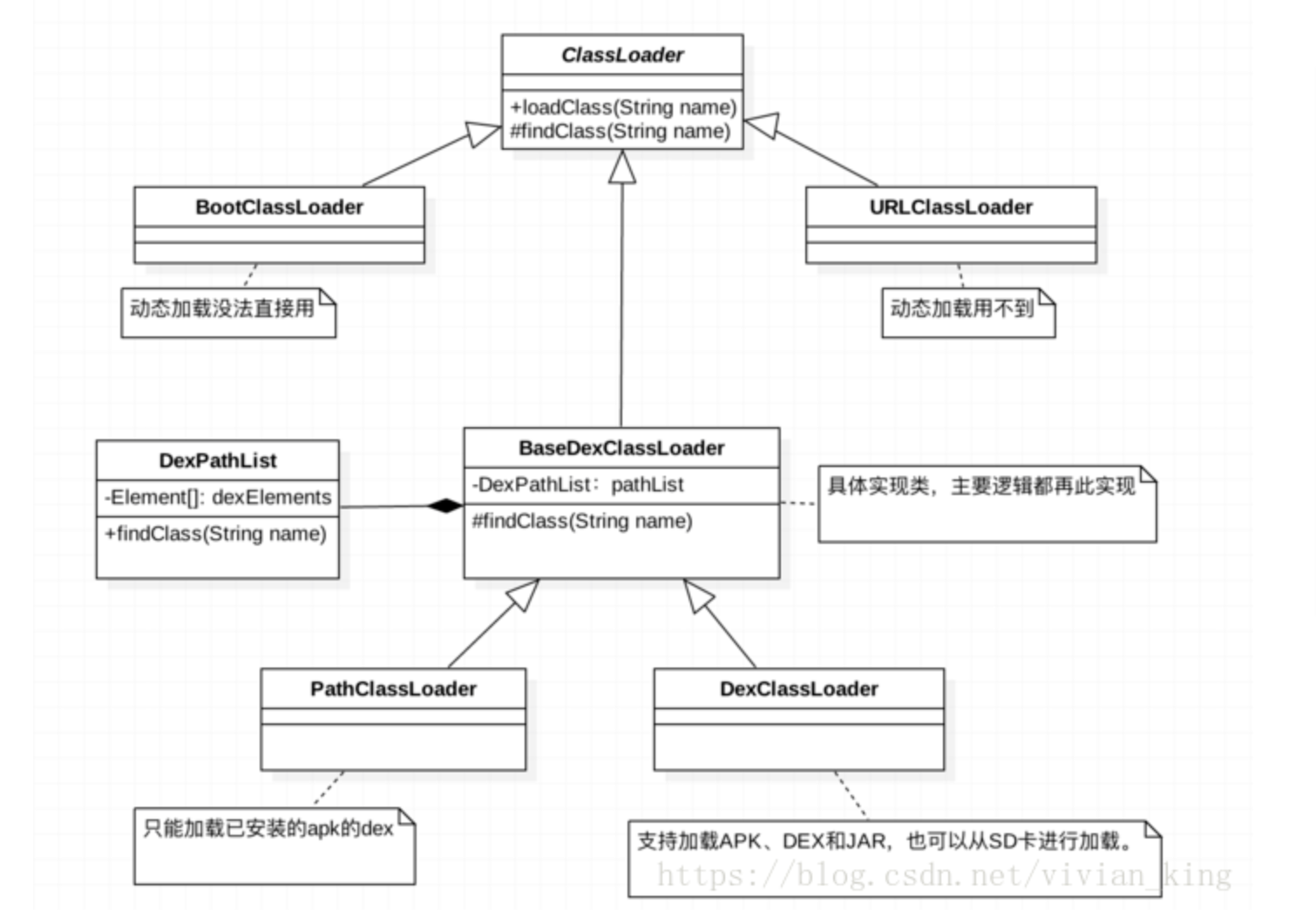
上面两个ClassLoader虽然包名都是java.lang.ClassLoader,但是Java中的是Java1.8中的代码,而Android平台上是Android API 26 Platform上的代码,虽然包名和类名都相同,但是两个类的实现并不相同。
下面根据源码是以Android平台上的代码来看的。 ClassLoader中有几个重要的方法。
- loadClass方法
/**
* Loads the class with the specified name. The
* default implementation of this method searches for classes in the
* following order:
* Invoke #findLoadedClass(String) to check if the class
* has already been loaded.Invoke the {@link #loadClass(String) loadClass} method
* on the parent class loader. If the parent is null the class
* loader built-in to the virtual machine is used, instead.
* Invoke the {@link #findClass(String)} method to find the class.
* If the class was found using the above steps, and the
* resolve flag is true, this method will then invoke the {@link
* #resolveClass(Class)} method on the resulting Class object.
*
* Subclasses of ClassLoader are encouraged to override {@link
* #findClass(String)}, rather than this method.
protected Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException
{
// First, check if the class has already been loaded
Class<?> c = findLoadedClass(name);
if (c == null) {
try {
if (parent != null) {
c = parent.loadClass(name, false);
} else {
c = findBootstrapClassOrNull(name);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// ClassNotFoundException thrown if class not found
// from the non-null parent class loader
}
if (c == null) {
// If still not found, then invoke findClass in order
// to find the class.
c = findClass(name);
}
}
return c;
}
注释中说的很明白,自定义classloader时,不应该去覆盖这个loadClass方法,而应该去override findClass方法。这个loadClass方法就决定了双亲加载机制的执行顺序。如果想要破坏双亲加载模型,去覆盖这个方法,修改加载顺序就可以了。
loadClass的最后一步是findClass,这个ClassLoader中并没有实际的业务实现,这个留待子类去实现,默认的实现会直接抛出ClassNotFoundException。
/**
* Finds the class with the specified <a href="#name">binary name</a>.
* This method should be overridden by class loader implementations that
* follow the delegation model for loading classes, and will be invoked by
* the {@link #loadClass <tt>loadClass</tt>} method after checking the
* parent class loader for the requested class. The default implementation
* throws a <tt>ClassNotFoundException</tt>.
*/
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
throw new ClassNotFoundException(name);
}
findClass中,用户自定义需要加载的Class的路径,然后将Class读取到内存中,转换成实际的Class,下面是一个实际的自定义的例子
public class DiskClassLoader extends ClassLoader {
private String mLibPath;
public DiskClassLoader(String path) {
mLibPath = path;
}
@Override
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
String fileName = getFileName(name);
File file = new File(mLibPath,fileName);
try {
FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream(file);
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
int len = 0;
try {
while ((len = is.read()) != -1) {
bos.write(len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
byte[] data = bos.toByteArray();
is.close();
bos.close();
return defineClass(name,data,0,data.length);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return super.findClass(name);
}
//获取要加载的class文件名
private String getFileName(String name) {
int index = name.lastIndexOf('.');
if(index == -1){
return name+".class";
}else{
return name.substring(index+1)+".class";
}
}
}
自定义的findClass方法中可以看到需要使用ClassLoader中的defineClass来将二进制流转换成实际的class,这个的源码比较繁琐,真有用到的细节的时候再来看吧。
上面说到Java和Android中ClassLoader的实现并不相同,但是上面两个业务核心类的实现逻辑基本是一致的,loadClass确定双亲加载模型的机制,findClass为子类加载不同路径、格式的class提供支持,从这个上面看,二者还是一脉相承的。
Java1.8与Android Platform上的SecureClassLoader和UrlClassLoader代码几乎完全一致,可以看到,google在java的classloader的基础上,为了满足加载自身dex格式文件的需求,保持双亲加载机制,自己实现了一套加载dex的classloader